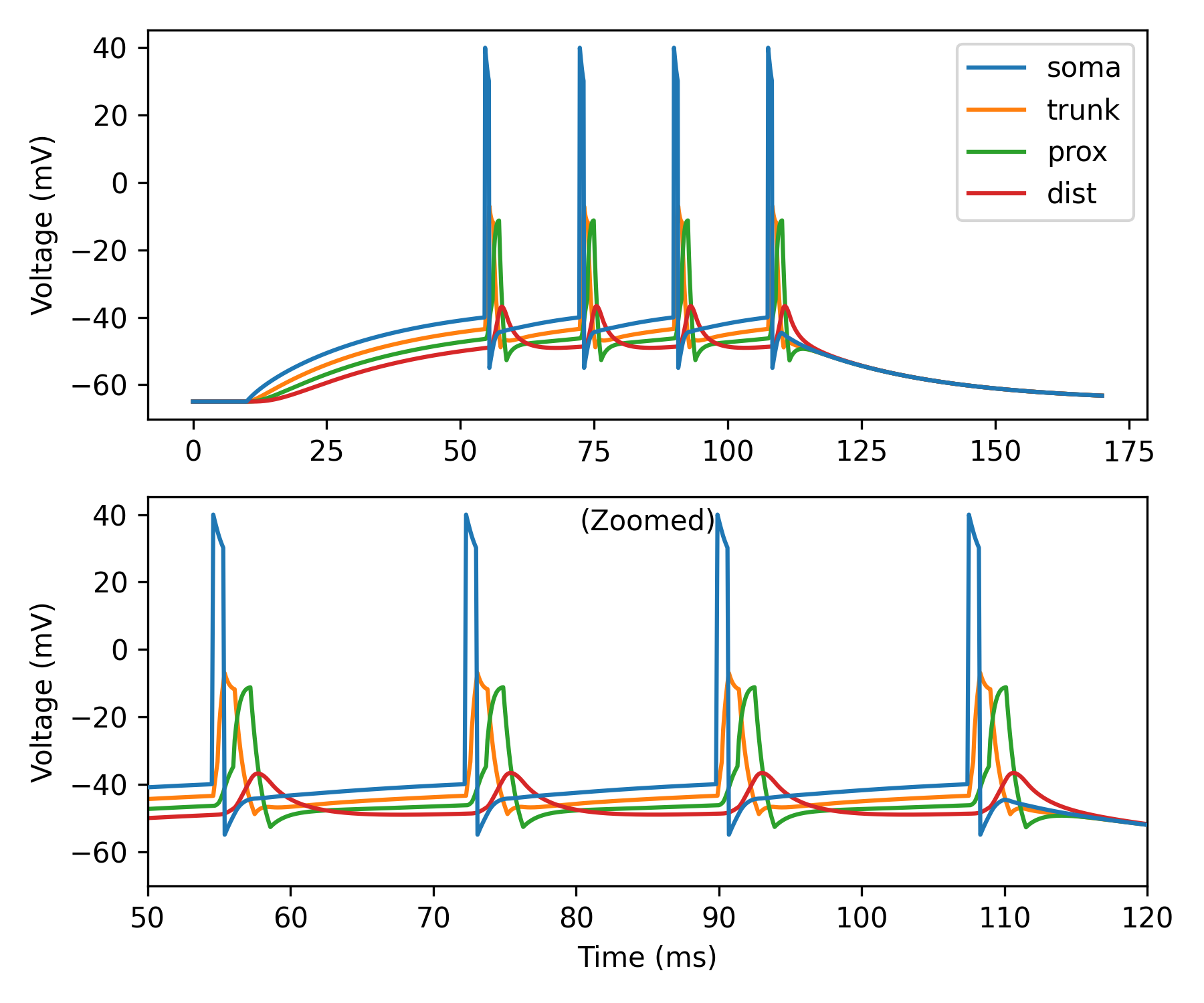
Back-propagating dSpikes#
An important property of biological neurons is that action potentials (APs) initiated in the axon can invade the soma and nearby dendrites and propagate backwards toward the dendritic tips. The transmission efficacy of these back-propagating action potentials (bAPs) relies on the dendritic morphology and the presence of dendritic voltage-gated ion channels.
In Dendrify, to achieve this behavior one needs to first recreate a more
realistic somatic AP shape by using the second_reset and spike_width
arguments in make_neurongroup. In this way, the somatic voltage can be first
reset to a more positive value and then below threshold. This allows the passive
depolarization of proximal dendrites in responses to somatic APs. If dendrites
are also equipped with active ionic mechanisms, this depolarization can trigger
the spontaneous generation of dendritic bAPs.
In this example we show:
How to implement back-propagating dSpikes in Dendrify.
How to achieve a more realistic somatic AP shape in I&F models, that is essential for the generation of bAPs.
Important
Notice that when a second_reset is used, the make_neurongroup method
returns an additional object which is Brian’s Synapses. If your simulation
code uses Brian’s Networks feature, this
additional object should be added to the network as well (also shown in the
example below).
import brian2 as b
from brian2.units import cm, ms, mV, nS, ohm, pA, uF, um, uS
from dendrify import Dendrite, NeuronModel, Soma
b.prefs.codegen.target = 'numpy' # faster for simple simulations
# Create neuron model
soma = Soma('soma', model='leakyIF', length=25*um, diameter=25*um)
trunk = Dendrite('trunk', length=100*um, diameter=2.5*um)
prox = Dendrite('prox', length=100*um, diameter=1*um)
dist = Dendrite('dist', length=100*um, diameter=0.5*um)
trunk.dspikes('Na', g_rise=22*nS, g_fall=14*nS)
prox.dspikes('Na', g_rise=9*nS, g_fall=5.7*nS)
dist.dspikes('Na', g_rise=3.7*nS, g_fall=2.4*nS)
con = [(soma, trunk, 15*nS), (trunk, prox, 6*nS), (prox, dist, 2*nS)]
model = NeuronModel(con, cm=1*uF/(cm**2), gl=40*uS/(cm**2),
v_rest=-65*mV, r_axial=150*ohm*cm,
scale_factor=2.8, spine_factor=1.5)
model.config_dspikes('Na', threshold=-35*mV,
duration_rise=1.2*ms, duration_fall=2.4*ms,
offset_fall=0.2*ms, refractory=5*ms,
reversal_rise='E_Na', reversal_fall='E_K')
# Make a new neurongroup
neuron, ap_reset = model.make_neurongroup(1, method='euler',
threshold='V_soma > -40*mV',
reset='V_soma = 40*mV',
second_reset='V_soma=-55*mV',
spike_width=0.8*ms,
refractory=4*ms)
# Record voltages
vars = ['V_soma', 'V_trunk', 'V_prox', 'V_dist']
M = b.StateMonitor(neuron, vars, record=True)
# Run simulation
net = b.Network(neuron, ap_reset, M)
net.run(10*ms)
neuron.I_ext_soma = 150*pA
net.run(100*ms)
neuron.I_ext_soma = 0*pA
net.run(60*ms)
# Visualize results
fig, axes = b.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(6, 5))
ax0, ax1 = axes
ax0.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_soma[0]/mV, label='soma', zorder=3)
ax0.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_trunk[0]/mV, label='trunk')
ax0.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_prox[0]/mV, label='prox')
ax0.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_dist[0]/mV, label='dist')
ax0.set_ylabel('Voltage (mV)')
ax0.legend()
ax1.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_soma[0]/mV, zorder=3)
ax1.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_trunk[0]/mV)
ax1.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_prox[0]/mV)
ax1.plot(M.t/ms, M.V_dist[0]/mV)
ax1.set_title('(Zoomed)', y=1, pad=-12, fontsize=10)
ax1.set_xlabel('Time (ms)')
ax1.set_ylabel('Voltage (mV)')
ax1.set_xlim(50, 120)
fig.tight_layout()
b.show()